Psoriasis on the face can affect your eyebrows, upper forehead, cheeks and part between nose & lips.
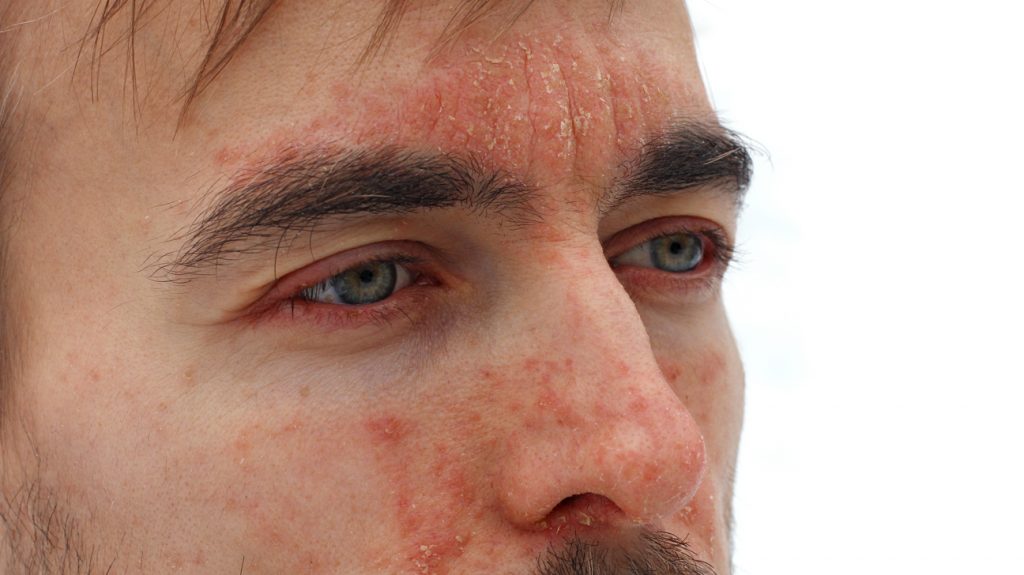
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that promotes rapid growth of skin cells. This might result in itchy, scaly spots that are thick and scaly. Symptoms might sometimes appear on the face.
Psoriasis is classified into different categories based on the appearance of the scales and their location on the body.
Face psoriasis can cause a wide range of symptoms and problems. Psoriasis on the face, in addition to medical complaints, can be very apparent, contributing to self-image issues and emotional difficulties in certain people.
However, there are a variety of treatments available to assist alleviate these symptoms.
Scalp psoriasis frequently leads to facial psoriasis.
Lesions may appear as red or purple painful spots that extend downward from the scalp. Silvery-white scales can appear on occasion.
Dead skin cells in the hair of a person with face psoriasis are common. This may appear to be dandruff caused by dry skin or skin sensitivity at first glance.
The following areas are the most typically affected by psoriasis on the face:
- the eyebrows
- the hairline
- the part in between the upper lip and nose.
- the upper forehead
Psoriasis of the face can sometimes spread to the eyelids and eyelashes. The eyelids may become discolored, swollen, and crusted as a result of this.
As a result, the eyelashes of a person may turn upward or downward. Eyelash rims that turn downward might put additional strain on the eye, causing inflammation.
A person may get psoriasis of the eyes in extremely uncommon conditions.
Psoriasis can also affect the lips, the insides of the cheeks, the gums, and the inside of the nose. These are frequently unpleasant and might impair a person’s ability to chew and swallow food.
Causes
While more research is needed to determine the specific aetiology of psoriasis, some scientists believe it is caused by inflammation in the body. Overproduction of skin cells and the formation of plaques on the skin may arise as a result of this.
Psoriasis is caused by the immune system’s T cells becoming overactive. Normally, this sort of cell defends the body against bacteria and other infectious agents.
However, when a person has psoriasis, the body activates T cells even if there is no infection. Different inflammatory reactions are then triggered by the T cells, causing skin cells to develop too quickly.
Treatments
Because the skin on the face is thin and sensitive, psoriasis on the face can be difficult to cure.
It’s critical that a doctor examines the skin and offers recommendations to ensure that the treatments aren’t too harsh or irritating to the skin on the face. Below mentioned are some treatment options for facial psoriasis:
-
Biologics
Biologic drugs may be used by people with moderate to severe psoriasis whose symptoms do not respond to topical or steroid therapies.
These disease-modifying drugs can slow the disease’s course and minimize the number of flares. They function by preventing the immune system from producing certain proteins or cells that cause inflammation.
-
Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids, such as hydrocortisone, are available over-the-counter (OTC). This could help to lessen the occurrence and severity of psoriasis on the face. People should, however, only utilize OTC topical steroids for a limited time.
-
Home cures and over-the-counter medications
In addition to steroids, saline solution face wash can also help to relieve pain and irritation.
There are a variety of over-the-counter remedies available, including:
- products for eliminating scale
- tazarotene cream or gel, an off-label treatment for acne that has been approved .
- UV light should only be used under the direction of a doctor.





